
below the Popliteus, or from the posterior tibial high up, or even from the popliteal. Peculiarities in Origin.The peroneal artery may arise 7 or 8 cm. It is covered, in the upper part of its course, by the Soleus and deep transverse fascia of the leg below, by the Flexor hallucis longus. It then runs behind the tibiofibular syndesmosis and divides into lateral calcaneal branches which ramify on the lateral and posterior surfaces of the calcaneus. below the lower border of the Popliteus, passes obliquely toward the fibula, and then descends along the medial side of that bone, contained in a fibrous canal between the Tibialis posterior and the Flexor hallucis longus, or in the substance of the latter muscle. It arises from the posterior tibial, about 2.5 cm. peronæa) is deeply seated on the back of the fibular side of the leg.
Peculiarities in Size.The posterior tibial is not infrequently smaller than usual, or absent, its place being supplied by a large peroneal artery, which either joins the small posterior tibial artery, or continues alone to the sole of the foot.īranches.The branches of the posterior tibial artery are: nearer the heel is the tendon of the Flexor hallucis longus. Next is the posterior tibial artery, with a vein on either side of it and lateral to the vessels is the tibial nerve about 1.25 cm. It is accompanied by two veins, and by the tibial nerve, which lies at first to the medial side of the artery, but soon crosses it posteriorly, and is in the greater part of its course on its lateral side.īehind the medial malleolus, the tendons, bloodvessels, and nerve are arranged, under cover of the laciniate ligament, in the following order from the medial to the lateral side: (1) the tendons of the Tibialis posterior and Flexor digitorum longus, lying in the same groove, behind the malleolus, the former being the more medial. In the lower third of the leg, where it is more superficial, it is covered only by the integument and fascia, and runs parallel with the medial border of the tendo calcaneus. It is covered by the deep transverse fascia of the leg, which separates it above from the Gastrocnemius and Soleus at its termination it is covered by the Abductor hallucis.
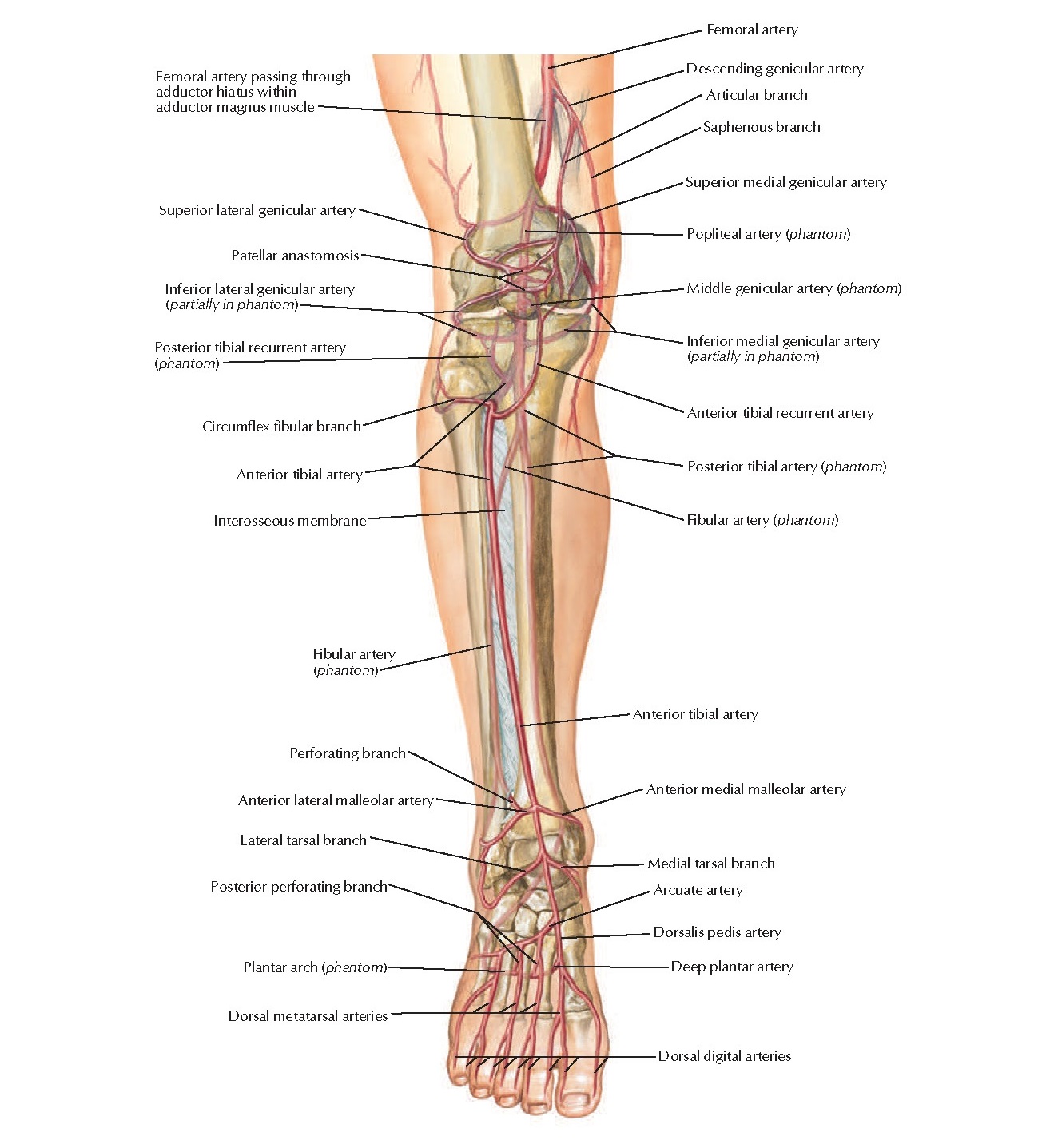
Relations.The posterior tibial artery lies successively upon the Tibialis posterior, the Flexor digitorum longus, the tibia, and the back of the ankle-joint. Here it divides beneath the origin of the Adductor hallucis into the medial and lateral plantar arteries. 551) begins at the lower border of the Popliteus, opposite the interval between the tibia and fibula it extends obliquely downward, and, as it descends, it approaches the tibial side of the leg, lying behind the tibia, and in the lower part of its course is situated midway between the medial malleolus and the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity. Tibialis Posterior)The posterior tibial artery (Fig.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
